Investigation of the Thermal Runaway in Vehicle Batteries
Thermal runaways in the HV batteries of electric and hybrid vehicles can lead to fires that are difficult to extinguish and endanger passenger safety. Extensive testing is required to ensure that HV batteries are designed safely with suitable protective mechanisms. In this application example you will learn how the necessary temperature measurements can be carried out at many points in the battery.

Background
If a battery cell in the HV battery heats up too much, chemical decomposition processes can occur in the cell. These trigger an irreversible chain reaction, which causes the cell to heat up suddenly (thermal runaway) and the high temperatures to spread to other cells (so-called thermal propagation). This leads to the destruction of the entire battery.
In order to prevent thermal runaways, extensive protective measures, such as the correct design of the cooling and heating system and heat-conducting elements between the cells, are taken into account during the development of the HV battery. For optimal design, the battery is tested for the risk of a thermal runaway. This is also done with provoked thermal runaways in the form of nail tests. Such tests require temperature measurements with a large number of sensors at numerous different points in the battery.
Measurement task
Acquisition of temperatures with hundreds of measurement points in HV batteries to detect crystallization points for thermal runaways and analyse protective measures.

Challenge
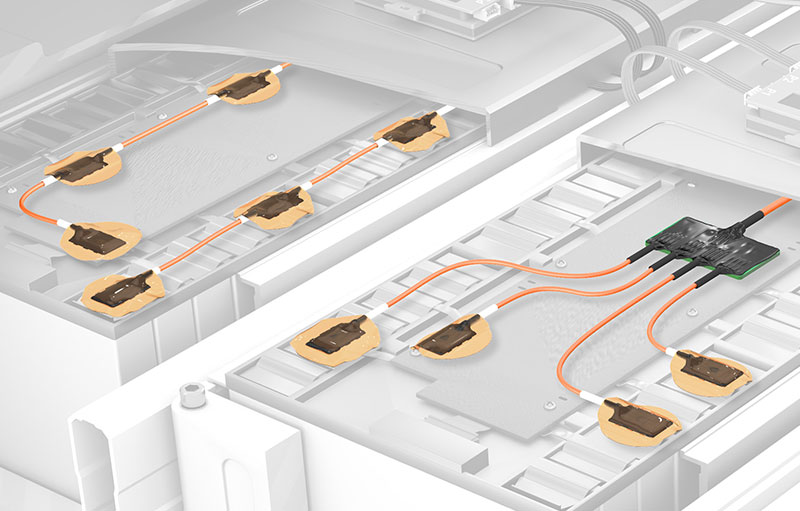
Simulations can be used to calculate the potential areas for very strong heat development (hot spots). In order to be able to investigate these areas metrologically, precise measurements are required at cell, module and pack level. Several hundred measurement points are involved. The sensors and necessary sensor cables must be designed very thinly in order to be able to measure in the restricted available space. The battery housing must not be excessively affected by the necessary holes for sensor cables in order not to falsify the measurements.
The CSM Measurement Solution
The HV DTemp Measurement System was developed for the digital and thus interference-free acquisition of up to 512 IC temperature sensors and enables precise thermal analysis for the prevention of thermal runaways.
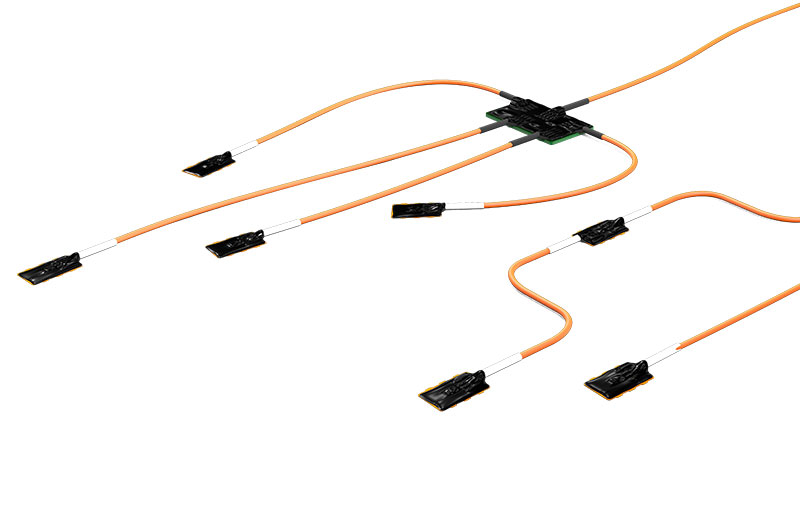
- Sensor Cable
Only one sensor cable led outside the battery is needed - HV DTemp-P Central Unit
Controls the system and transfers the data via CAN to the DAQ software - IC Senors on ultra-thin flexible circuits
Exact positioning of sensors and precise temperature measurement between battery cells - Single IC Sensors
Measures temperatures at separated measurement points - HV DTemp-Mx Controller
Connection for up to 64 IC temperature sensors
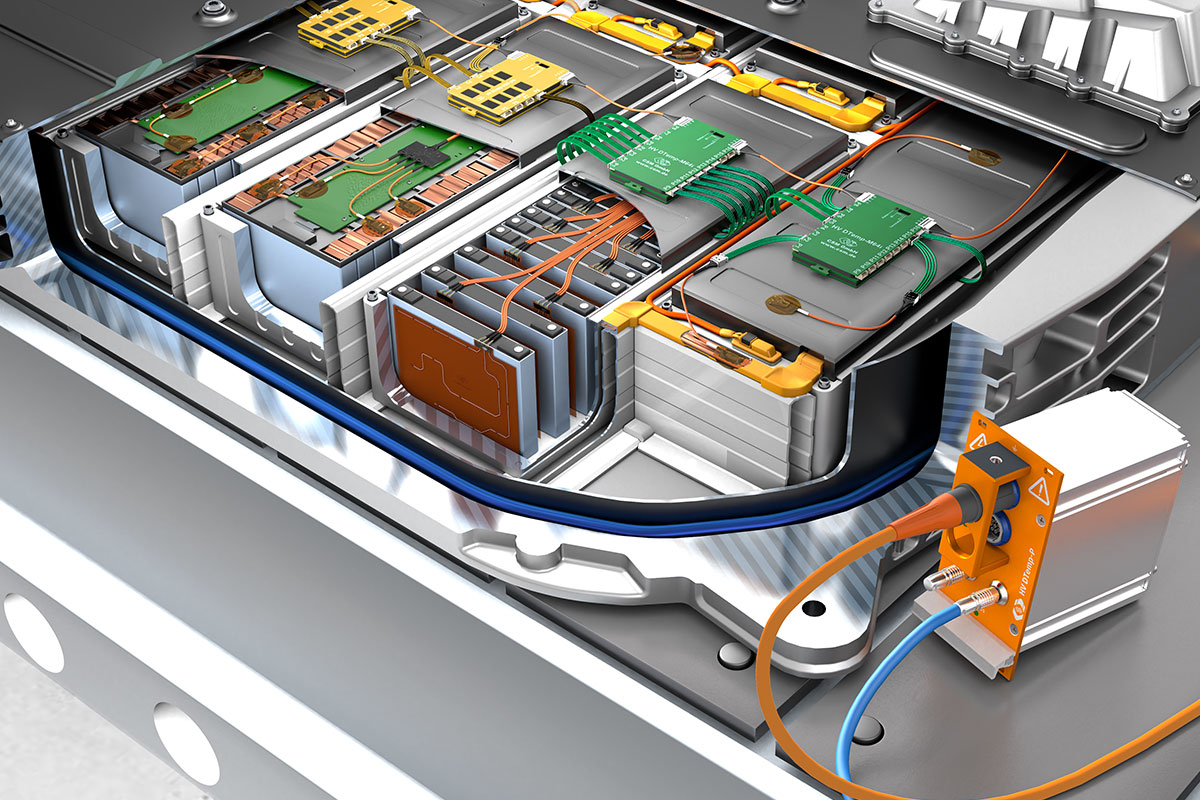
- With the HV DTemp IC Sensors the temperatures are measured at the calculated measurement points in the HV battery. The IC Sensors consist of IC-temperature sensors, which are mounted on ultra-thin flexible circuit. For the different measurement points special variants of the IC Sensors are available:
- With single sensors separate components such as connectors, electronic modules and special housing points can be tested for heating. The single sensors are equipped with a sensor cable for direct connection to HV DTemp-M Controller.
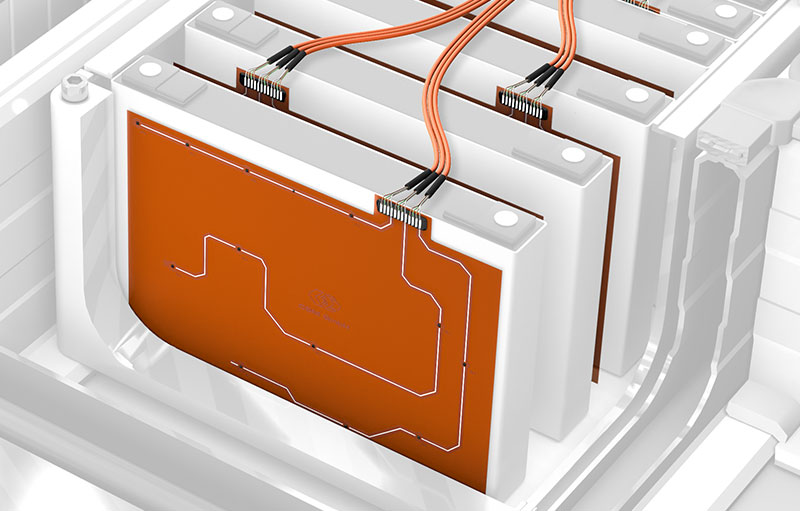
- Sensor assemblies are suitable for equipping individual, adjacent measurement points on conductor rails, module surfaces or connecting lines. For this purpose, up to four individual IC sensors are connected in series or via a small distributor board.
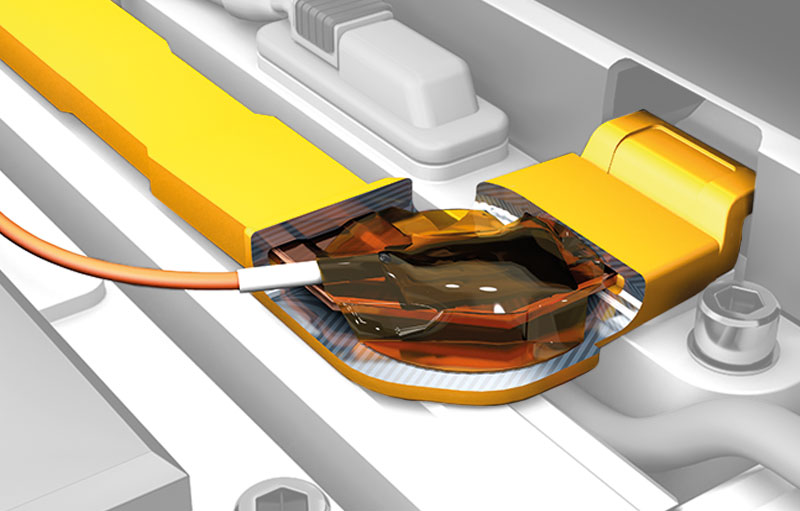
- IC sensors on ultra-thin flexible circuit are used for planned and precisely positioned measurements between the battery cells.
- The HV DTemp IC sensors are connected via HV DTemp-Mx Controller. Up to 64 sensors can be connected to one controller and up to 8 controllers can be cascaded.
- Via only one HV-safe sensor cable all controllers are connected to the HV DTemp-P Central Unit. Since only one breakthrough for the sensor cable into the battery housing has to be created, the housing structure is only slightly affected and gas tightness is maintained.
- The HV DTemp-P Central Unit can easily be connected to further measurement modules via the CAN bus. If, for example, extremely high temperatures have to be recorded at a provoked thermal runaway, HV-safe temperature measurement modules HV TH8 evo can be connected.
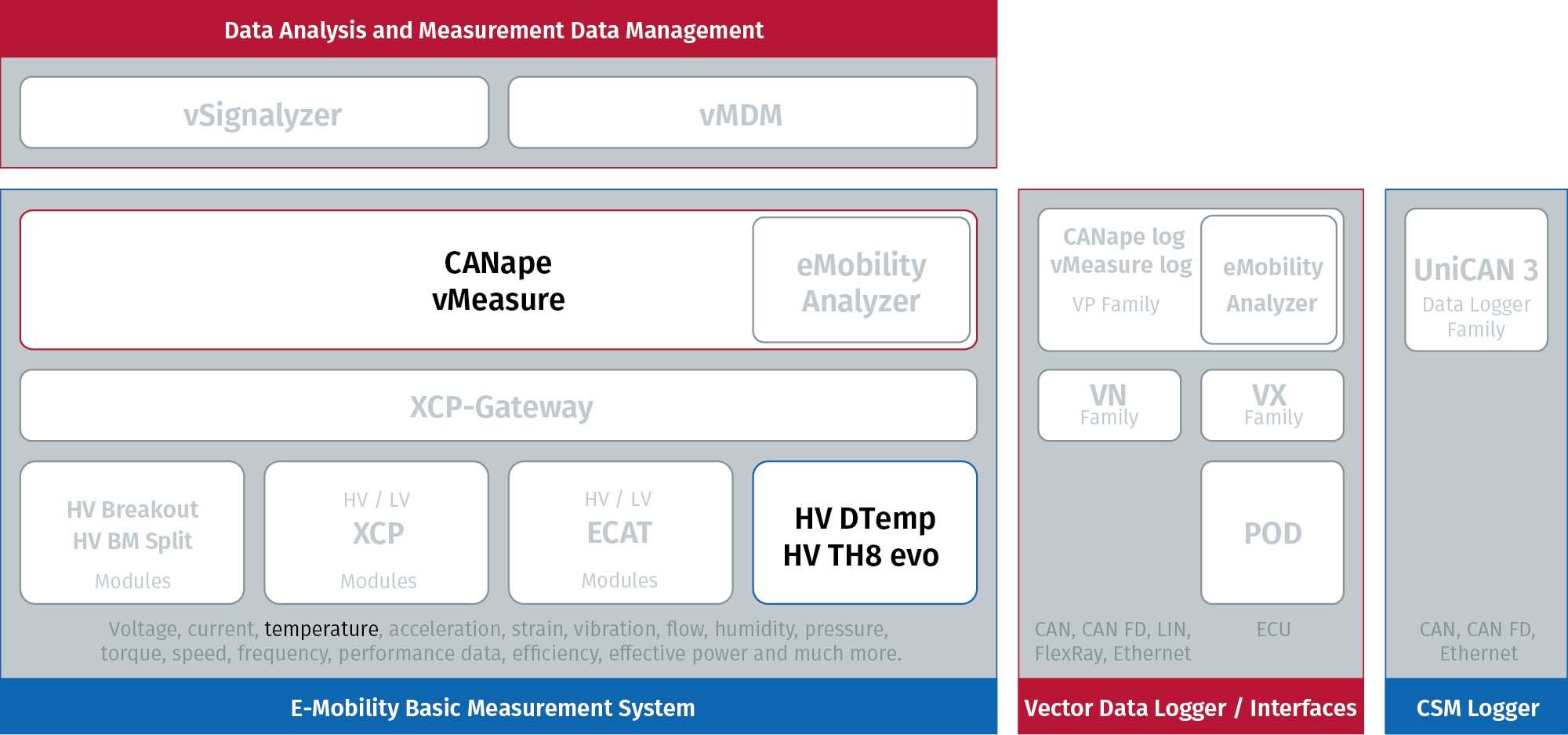

Benefits
With the HV DTemp measurement system, temperatures can be measured at all relevant points in the HV battery and instrumentation is greatly simplified. IC sensors on ultra-thin flexible circuit can be positioned precisely and reproducibly. In addition, the flexible circuits can be easily inserted during the assembly of the battery. Precise temperature measurements can be used to verify the measures taken to prevent thermal runaways and ensure the safety of the vehicle and passengers.
More Information
Related Products
Related Hardware

The Vector CSM E-Mobility Measurement System
The measurement system for the development of electric mobility

HV DTemp Measurement System
Digital temperature measurement with up to 512 measurement points
The CSM HV DTemp measurement system is designed for the digital and precise measurement of up to 512 temperature measurement points via a single cable connection to the HV DTemp Central Unit.

HV TH Measurement Modules
Safe temperature measurement with K-type thermocouples
Safe temperature measurements with thermocouples on high-voltage components: the high-voltage-safe temperature measurement modules are specifically designed for the reliable acquisition of temperatures in electric and hybrid vehicles.
Related Software
vMeasure
Reliably Solving Complex Measurement Tasks
vMeasure, developed by Vector Informatik, is an easy-to-use software tool for the acquisition and analysis of measurement data that can be used in combination with all CAN- and EtherCAT®-based CSM measurement modules. CSMconfig was integrated directly to ensure swift configuration.


Swift configuration of measurement chains: CSMconfig is the reliable configuration software for all CAN and EtherCAT® based measurement modules from CSM. The clearly arranged and easy-to-use user interface allows an easy setting of all measurement parameters. This helps speeding up the measurement setup considerably.

 Home
Home Newsletter
Newsletter