Thermal testing of HV batteries
Understanding and Early Prevention of Thermal Runaway
The mobility transition is essentially determined by the battery-powered, electric drivetrain – the optimization of the HV battery is therefore an important adjusting screw. One parameter is the focus of testing: temperature. It is relevant for the flawless and efficient operation of the vehicle. Valuable findings for the safety and correct design of the system can be derived from observing the thermal behavior. This is a good reason to perform detailed and close-meshed measurements of the temperatures inside a traction battery.

Why measure temperatures?
The use of an HV battery in a vehicle requires consideration of many aspects, including whether safe operation is possible in every conceivable scenario. One emergency that should be avoided at all costs is a “thermal runaway”. In this case, a malfunction of the battery cells leads to a chemical chain reaction and an uncontrolled and unstoppable fire in the battery. Failure to prevent or predict this in time can lead to considerable damage to property and personal injury. For this reason, the individual situations that can lead to a thermal runaway are examined in detail. These include, in particular, the temperature effect on the neighboring cells and modules as well as the heat transfer and accumulation within the battery.
Important influencing factor
The performance of high-voltage lithium-ion batteries is significantly influenced by temperatures due to their chemical properties - the optimum range is from 15 °C to 35 °C. At lower temperatures, the chemical processes in the battery are significantly slowed, which reduces the energy and power capacity – high temperatures also have a negative effect, as they can destroy the battery in extreme cases. One source of high temperatures is self-heating, which is caused by entropy changes and ohmic losses when charging and discharging the battery. As a result, over time different temperatures occur during different load conditions. The spatial distribution of temperatures is also by no means uniform: even within a single cell, they differ significantly in different areas. Dangers can arise from locally limited areas, so-called “hot spots”, with very high temperatures. These increase the risk of internal short circuits and affect all typical cell designs equally.
Measurement task
Acquisition of temperatures with hundreds of measurement points in HV batteries in order to precisely investigate temperature curves.

Many measurement points with the fewest interventions possible
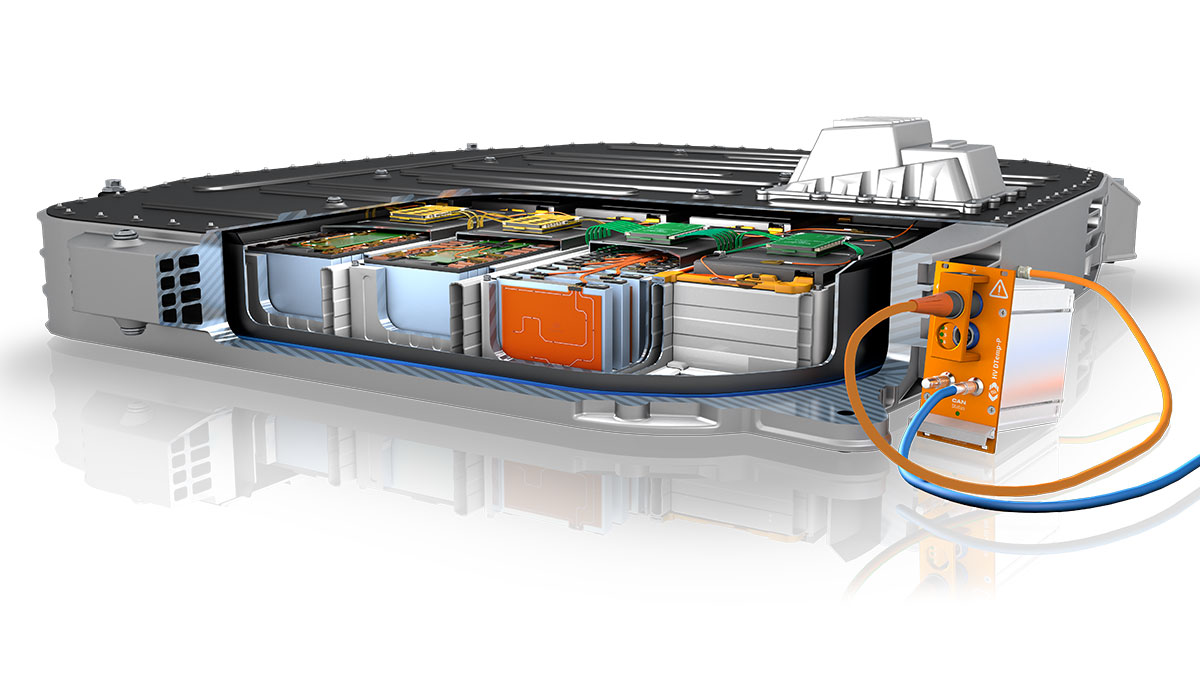
Various types of batteries, including cylindrical, pouch or prismatic cells, are currently found in the traction batteries of electric vehicles. Scalable measurement technology that offers suitable sensors for all these concepts is desirable for the necessary measurements during the various development phases. Although this close-meshed monitoring of many temperatures on all components of the HV battery provides a very precise picture of the thermal processes, it also means that many measurement points have to be installed in a very confined space. At the same time, the sensors and their sensor cables must be small enough to be positioned between the cells. There is also another safety aspect to consider: The entire measurement setup must be safe for use in the high-voltage (HV) environment so that personal protection when working on the HV battery meets the necessary safety standards.
Measure at up to 512 points - with just one sensor cable
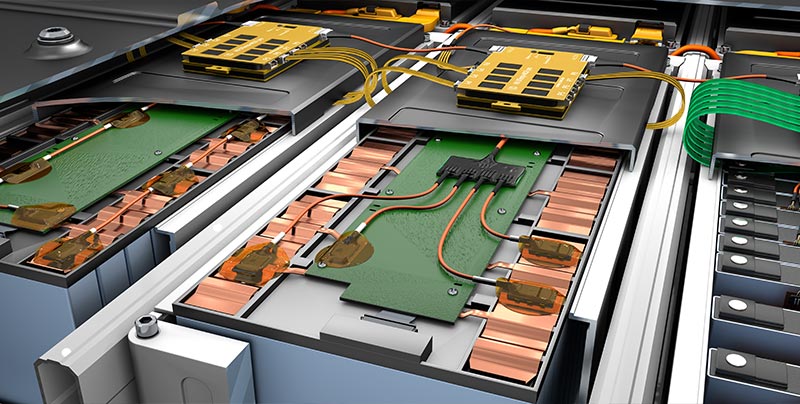
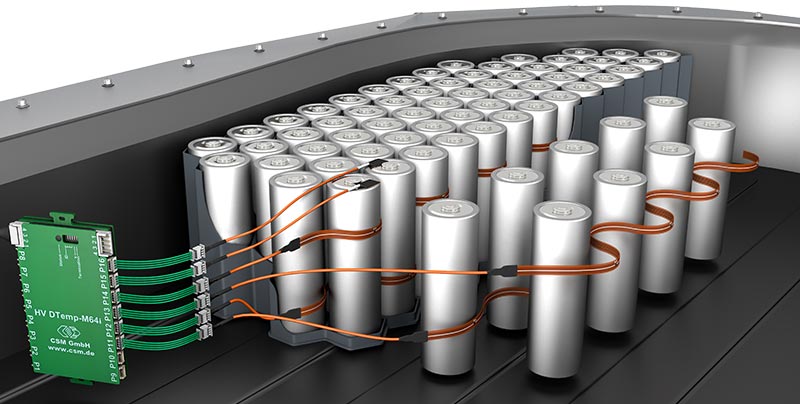
With the HV DTemp measurement system, comprehensive and precise temperature measurement in HV batteries can be performed safely. It enables the precise, digital, and interference-free acquisition of up to 512 temperature measurement points with a single sensor cable to the HV DTemp-P central unit. With miniaturized and interference-free IC temperature sensors, the overall system not only offers a measurement accuracy of ±0.1 °C to ±0.25 °C, they can also be applied particularly flexibly. Depending on the application, there are individual options for how the sensors can be installed, for example as encapsulated individual sensors or mounted on an ultra-thin flexible circuit - ideal for measurements between different cell types.
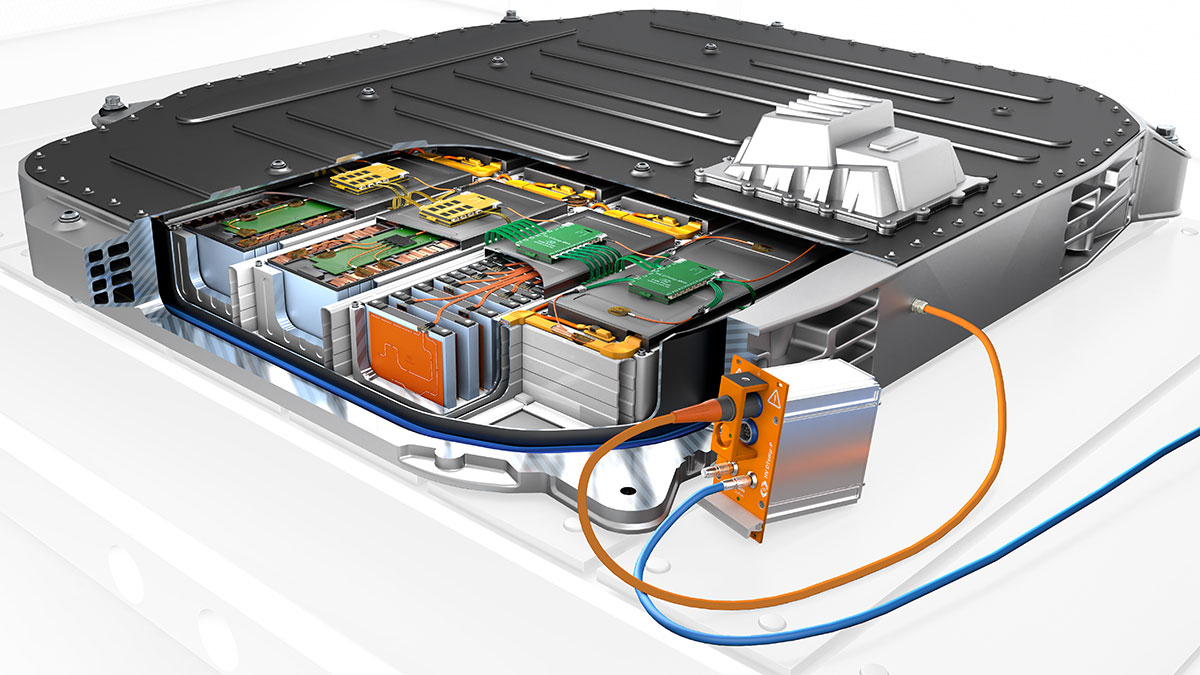
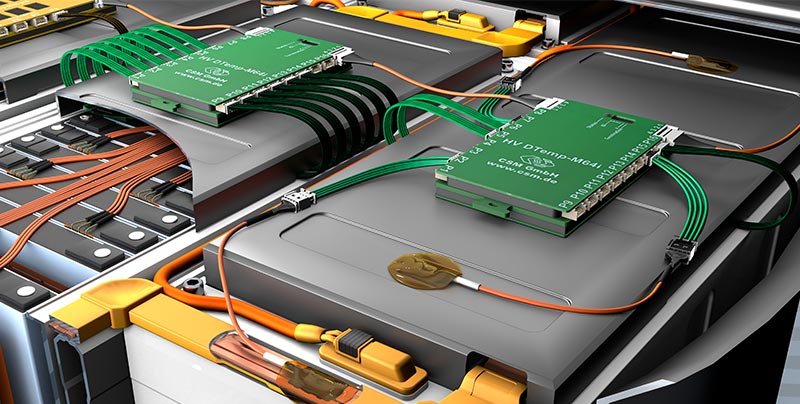
An easily scalable system
Up to four IC temperature sensors can be connected as a sensor assembly to detect temperatures on the battery housings. These are either installed in series or connected via a small distribution board. The HV DTemp IC sensors are connected via HV DTemp Controllers. Up to 16 sensor assemblies (corresponding to 64 temperature sensors) can be connected to one controller and up to eight controllers can be cascaded: They therefore provide connections for up to 512 temperature sensors. The controllers address the sensors, supply them with voltage and forward the temperature values to the central unit. All HV DTemp Controllers are connected to the central unit via a high-voltage-safe sensor cable. All that needs to be done is to drill one hole with a cable gland in the battery housing. The HV DTemp-P Central Unit records the data from the HV DTemp Controllers and ensures high-voltage safety through galvanically isolated inputs. The measurement data is transferred to the measurement computer via CAN.



Analyze HV batteries precisely and comprehensively
All components of the HV DTemp system have a compact and robust design. As only one measurement module is required outside the battery, the system has a space-saving design with minimal impact on the measurement object. The sensors can be positioned between the cells, allowing the precise acquisition of temperature curves. The arrangement of the sensors on an ultra-thin flexible circuit can be repeated exactly from cell to cell. The scalable system also offers further areas of application in the HV environment - for example, temperature measurements on other components of the electric powertrain, such as the inverter.
More information
Related Products
Related Hardware

HV DTemp Measurement System
Digital measurement with up to 512 measurement points
The CSM HV DTemp measurement system is designed for the digital and precise measurement of up to 512 measurement points - temperature or humidity - via a single cable connection to the HV DTemp-P Central Unit.

The Vector CSM E-Mobility Measurement System
The measurement system for the development of electric mobility
Related Software
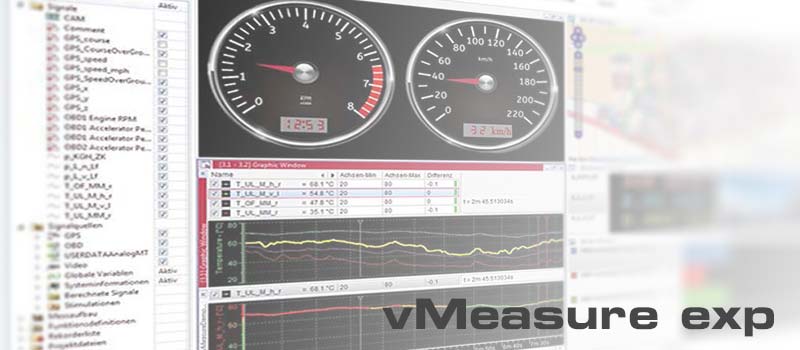
vMeasure
Reliably Solving Complex Measurement Tasks
vMeasure is a subset of CANape focused on measurement. It is an easy-to-use software tool for the acquisition and analysis of measurement data that can be used in combination with all CAN- and EtherCAT®-based CSM measurement modules. CSMconfig was integrated directly to ensure swift configuration.


Swift configuration of measurement chains: CSMconfig is the reliable configuration software for all CAN and EtherCAT® based measurement modules from CSM. The clearly arranged and easy-to-use user interface allows an easy setting of all measurement parameters. This helps speeding up the measurement setup considerably.

 Home
Home