CNT evo CAN MM Series
Simple acquisition of digital measurement variables
The CNT evo is a high-precision measurement module designed for measuring frequencies, pulse widths, incremental displacement measurements, rotation angles, position measurement, event counting and period measurements.
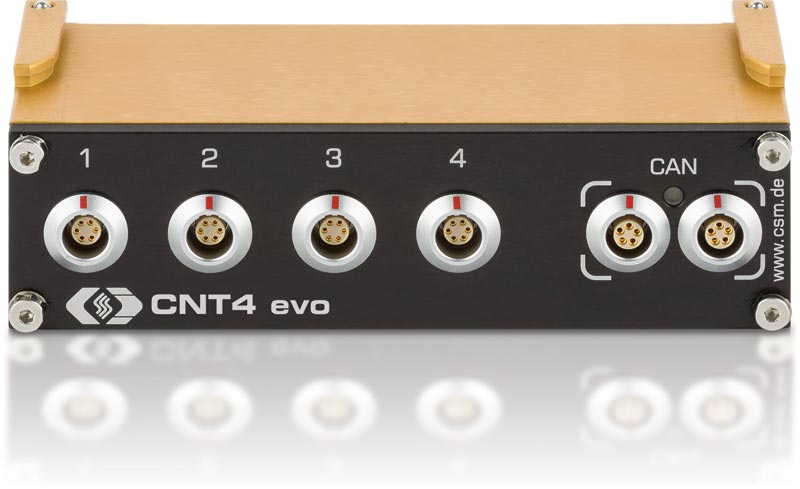
CNT4 evo
CSM’s CNT4 evo measurement module supersedes the previous versions of CNT4 releases. Its functional range is unchanged and now supports TEDS-capable sensors. Another added capability is the separate setting of CAN ID and measurement data rate for each channel.
The CNT4 evo features four electrically isolated measurement inputs and therefore 8 logical channels for measuring:
- Frequencies: 0.1 Hz to 300 kHz
- Cycle / pulse duration: 1 µs to 50 s
- Duty cycle / PWM: 0 % to 100 %
- Event counting: 0 to 16 bit (65,535) or up to 32 bit
- Speed: 0.01 rpm to 600,000 rpm
- Time offsets: 1 µs to 50 s
- Up and down counting via pulse/direction or quadrature signal.
Each physical channel can read two measurement values simultaneously, which means that CNT evo modules provide eight logical channels. On/off trigger thresholds are adjustable per channel and feature a switchable AC coupling. Also, these modules are equipped with a galvanically isolated sensor excitation.
Housing variants
| Designation | Case eXtra Small (CXS) | Case Small (CS) | Slide Case Small (SCS) | Case Large (CL) | Slide Case Large (SCL) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNT4 evo |
Successor models
You are already using the measurement modules CNTMM 4 classic and pro and would like to know which of the CNT4 evo modules would be a possible successor? Just have a look here.
Downloads
Downloads
Firmware for CNT4 CAN modules, HW revision B
- Configuration software for CSM measurement modules (incl. documentation)
- with visualization software CSMview
- System requirements:

 Home
Home