
Menu
- News
- Fields of Application
- Products
- Support
- Downloads
- Company
- Contact

Offering long ranges for electric cars is one of the biggest challenges for vehicle manufacturers. The decisive factor here is the total energy consumption of the vehicle. Often, only the consumption of the electric powertrain is considered, but: How much does the low-voltage vehicle electrical system, which includes driver assistance systems and infotainment, contribute to discharging the drive battery? For competitive analyses, the currents of these components were therefore examined in more detail: Around 100 CSMshunts of different variants were used for benchmarking an e-SUV.


For benchmarking of production vehicles, various properties are investigated in order to be able to compare vehicles from different manufacturers. Such procedures are often carried out by experienced development service providers, such as AVL, one of the world's leading mobility technology companies for development, simulation and testing in the automotive industry. One aspect that was analyzed in this context for a battery-electric SUV was the power consumption of the electrical subsystems in the low-voltage on-board network, i.e. for the 12 V and 48 V DC voltage levels.
This includes, for example, the control units, driver assistance systems (ESP, ABS), windshield wipers, the power windows, the car's locking system, as well as the navigation system and infotainment. Since the low-voltage system is connected to the high-voltage traction battery and is supplied by the DC/DC converter, this energy consumption contributes to the range reduction of the vehicle.
Measurement Task
Acquisition of current and voltage at various components for consumption calculation as well as temperatures in the vehicle interior.

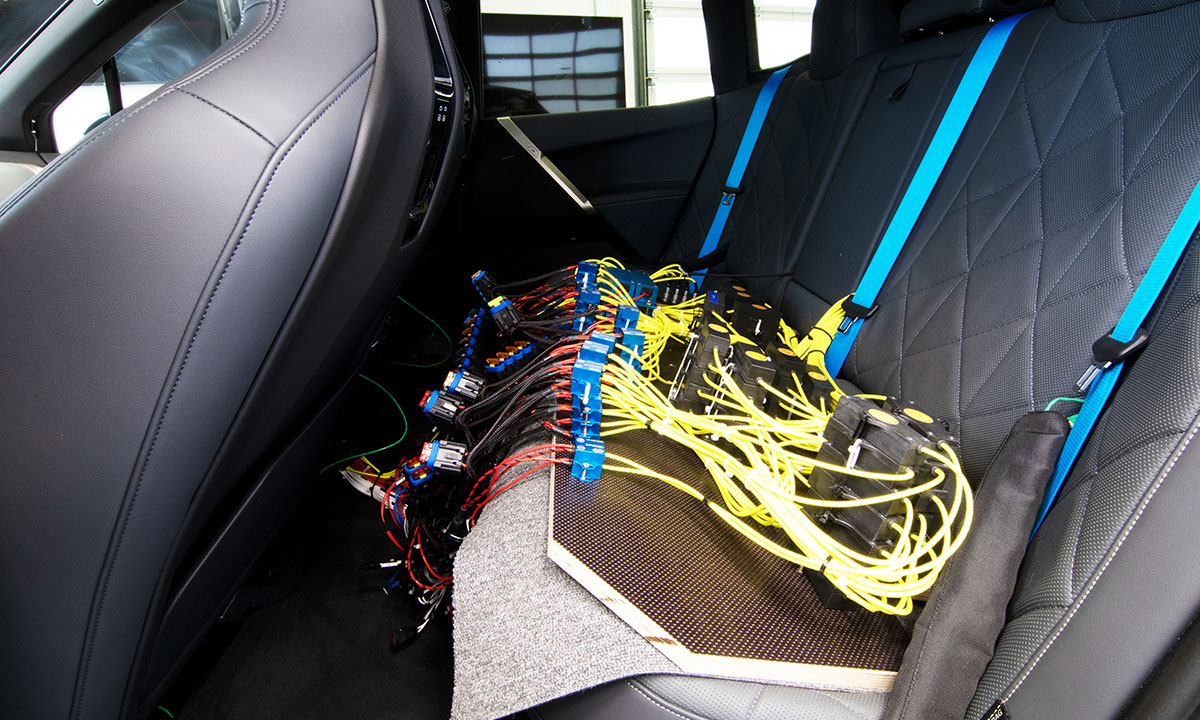
For the analysis of power consumption in the low-voltage range, all supply lines of all consumers had to be equipped with measurement resistors, known as "shunts", in order to precisely determine the current consumption of the individual consumers. Due to high-quality, special electrical equipment, the complete analysis of the low-voltage electrical system thus involved a large number of measurement points.
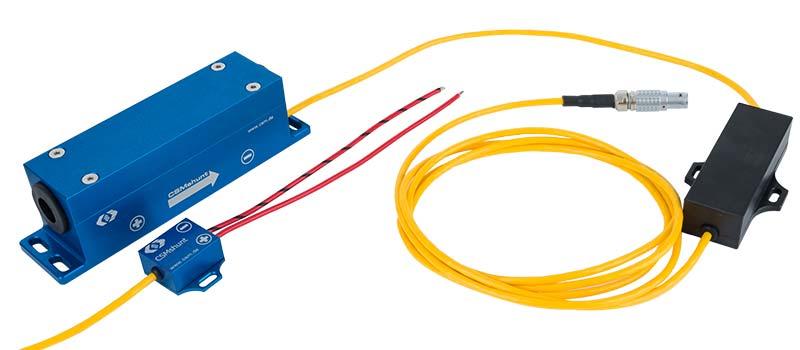
More than 100 CSMshunts were installed to benchmark the energy consumption of all components in the low-voltage range. For the smaller currents up to 25 A, the CSMshunt fuse was used: these could be easily integrated into the existing connector system of the vehicle‘s fuse box. Larger CSMshunts were used for the higher currents up to 125 A of the vehicle electrical system. All shunt variants already have an integrated measuring amplifier for the falling voltages and thus offer high resolution and accuracy.
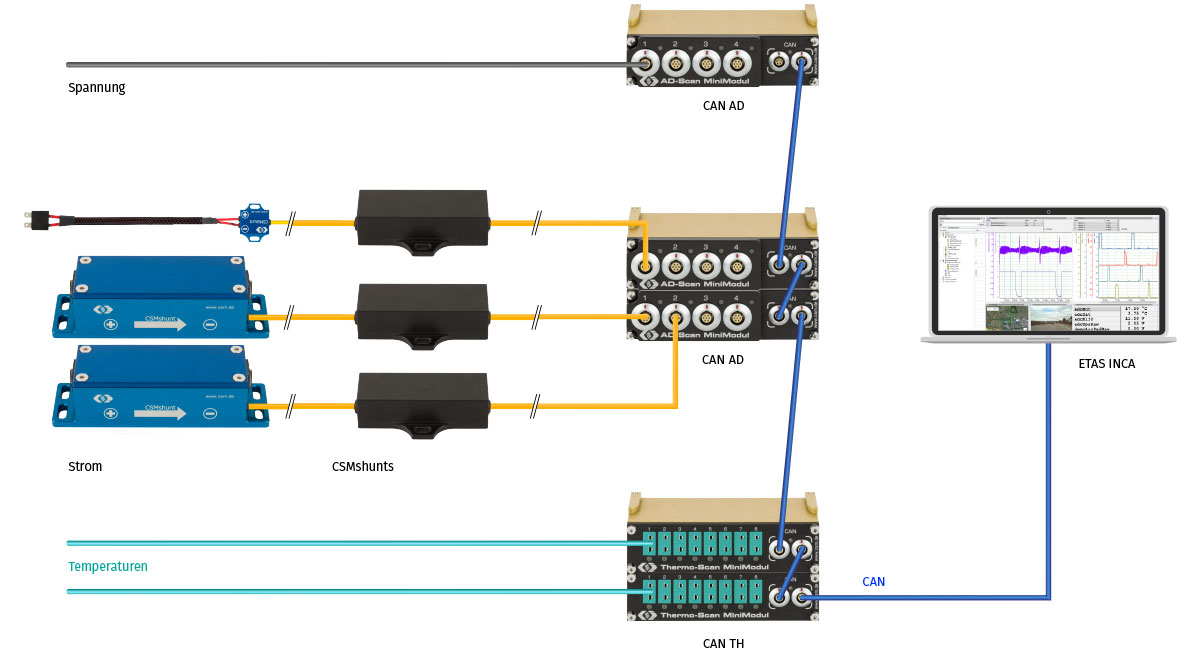
With the CSM AD measurement modules, the currents were calculated from the falling voltages at the shunts and passed on via CAN. With another AD module, also via CAN, the supply voltage of the respective components was recorded. The analysis software then calculated the respective power consumption from the measured values. In addition, temperatures were recorded in the vehicle interior using thermocouples and THMM thermal modules. Via an ETAS CAN interface, the CAN data were bundled and transmitted to a computer for analysis with INCA.
Especially with a large amount of measurement technology, compatibility and easy configuration are particularly important for us. Vehicle testing is a complex business with many players - so it is crucial to be flexible and efficient at the same time. That's why we appreciate the cooperation with CSM: Here we get the complete package of high-quality hardware and individually adapted software solutions.
Christian Juwan, Product Manager Vehicle Benchmarking, AVL
The average power consumption of the vehicle electrical system was around 500 watts: In addition to the control of vehicle functions (lighting, windshield wipers, power windows, door openers), the air conditioning and heating systems as well as the infotainment system consumed the most power.
As the number of electrical components in the low-voltage electrical system increases, manufacturers must also consider energy-saving measures, such as automatic, intelligent switch-on and switch-off systems in line with typical user usage. How these are implemented and what other energy management strategies are applied was part of the benchmarking evaluation.

With the CSMshunts and the AD modules, the currents of all consumers in the low-voltage range of the vehicle could be measured easily and reliably. With the different variants, the appropriate measuring resistor could be selected according to requirements. Due to their robust design, both the shunts and the measurement modules were suitable for applications in road tests and on the test bench.



Fast and precise measurements with ETAS INCA: Both software complements CSM INCA AddOn CAN and CSM INCA AddOn ETH enable easy integration of the CSM measurement modules and the ECM exhaust measurement modules in the measurement and calibration software INCA from ETAS.


Swift configuration of measurement chains: CSMconfig is the reliable configuration software for all CAN and EtherCAT® based measurement modules from CSM. The clearly arranged and easy-to-use user interface allows an easy setting of all measurement parameters. This helps speeding up the measurement setup considerably.